Understanding the causes of sore knees is essential for finding appropriate treatment and relief. From overuse injuries to underlying medical conditions, there are various factors that can contribute to knee pain. By delving into the root of the problem, individuals can take proactive steps to manage and alleviate their discomfort.
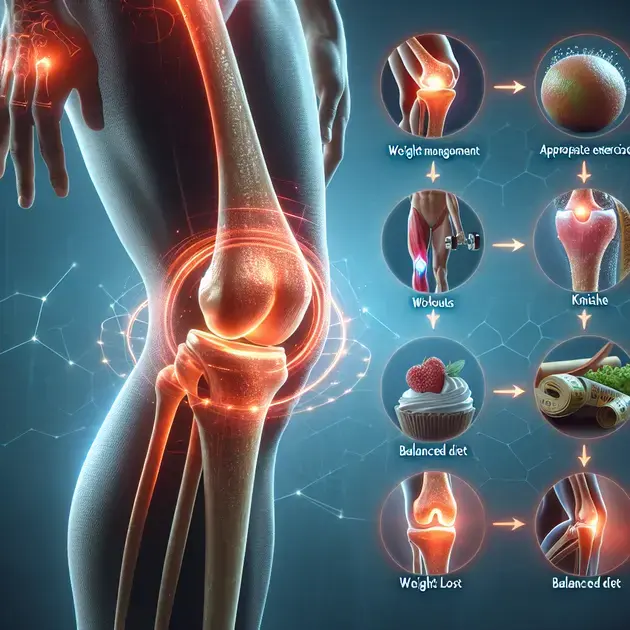
Recent studies have shown a strong correlation between excess weight and knee pain. The additional strain on the joints from carrying extra weight can lead to increased pressure and potential damage. This highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy weight to prevent unnecessary stress on the knees and reduce the risk of developing chronic pain.
Understanding the Link Between Overuse and Sore Knees
Overuse is a common cause of sore knees, especially in individuals who engage in repetitive high-impact activities such as running, jumping, or squatting. Understanding the link between overuse and knee pain is crucial for preventing injuries and maintaining knee health.
Step-by-Step Guide:
1. Assess your current exercise routine and identify any activities that may be putting excessive strain on your knees. Websites like Runner’s World offer valuable insights on proper running techniques to prevent knee overuse.
2. Incorporate low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling into your fitness regimen to give your knees a break from high-impact stress. Apps like Peloton and Strava provide guided cycling workouts that are gentle on the knees.
3. Invest in proper footwear with adequate cushioning and support to reduce the impact on your knees during physical activities. Brands like Nike and Asics offer specialized sneakers for various sports that can help prevent knee pain.
4. Listen to your body and give yourself enough rest between intense workouts to allow your knees to recover. Fitness apps like MyFitnessPal have features to track your exercise intensity and recommend rest days for optimal recovery.
5. Consult with a sports medicine specialist or physical therapist if you experience persistent knee pain to address any underlying issues and develop a personalized treatment plan. Platforms like Zocdoc can help you find reputable healthcare providers in your area.
Exploring the Connection Between Excess Weight and Knee Pain
Excess weight can significantly contribute to knee pain due to the increased pressure and stress placed on the knee joints. Exploring the connection between excess weight and knee pain highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy weight for overall knee health.
Step-by-Step Guide:
1. Calculate your body mass index (BMI) using online tools such as the CDC’s BMI calculator to determine if you are in a healthy weight range. Understanding your BMI can help you gauge the impact of excess weight on your knees.
2. Follow a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains to support weight management and reduce inflammation that can contribute to knee pain. Apps like MyPlate and Lose It! offer meal tracking and nutritional guidance to help you make healthier food choices.
3. Engage in regular physical activity to not only aid in weight loss but also strengthen the muscles around your knees for better support and stability. Fitness platforms like Fitbit Coach and Beachbody provide workout programs tailored to different fitness levels and goals.
4. Avoid prolonged periods of sitting or standing to alleviate pressure on your knees and promote circulation. Use ergonomic tools like standing desks or apps like Stand Up! The Work Break Timer to remind you to change positions throughout the day.
5. Join a support group or seek counseling if emotional eating or body image issues are impacting your ability to maintain a healthy weight. Websites like Overeaters Anonymous offer virtual meetings and resources for overcoming emotional barriers to weight management.
Uncovering the Role of Maintaining a Healthy Weight in Knee Health
Maintaining a healthy weight plays a crucial role in preserving knee health by reducing the risk of developing conditions like osteoarthritis and joint degeneration. Uncovering the significance of maintaining a healthy weight sheds light on the long-term benefits for your knees and overall well-being.
Step-by-Step Guide:
1. Set realistic weight loss goals based on recommendations from healthcare professionals or weight management apps like Noom or WW (Weight Watchers). Establishing achievable targets can keep you motivated to stay on track.
2. Monitor your progress regularly by tracking your weight, meals, and physical activity using online tools or apps like MyFitnessPal. Keeping a record of your habits can help you identify areas for improvement and celebrate your successes.
3. Prioritize sleep and stress management to prevent emotional eating or unhealthy coping mechanisms that may hinder your weight maintenance efforts. Meditation apps like Headspace or Calm can assist in reducing stress and promoting mindfulness.
4. Consult with a registered dietitian or nutritionist to create a personalized meal plan that supports your weight management goals and addresses any nutritional deficiencies. Websites like EatRight.org can help you find accredited professionals in the field.
5. Stay physically active through enjoyable and sustainable forms of exercise like dancing, hiking, or yoga to support weight maintenance and overall joint health. Online platforms such as Yoga With Adriene and Dance Church offer virtual classes for all fitness levels.
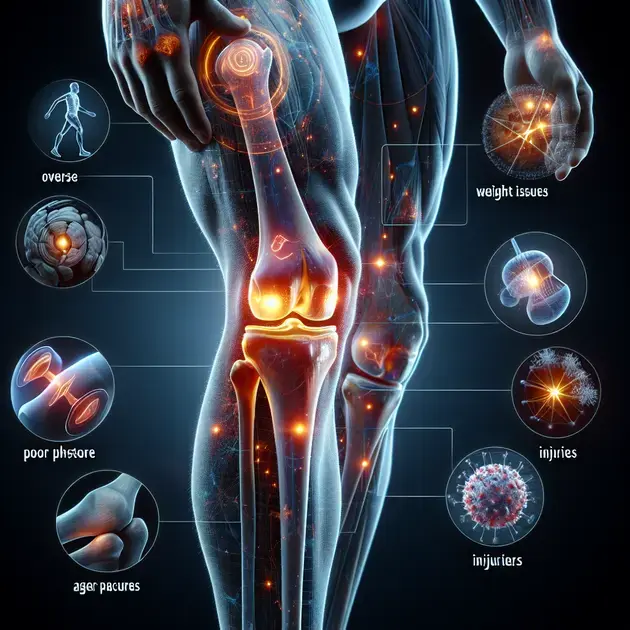
**Common Factors Contributing to Knee Discomfort**
Introduction
Knee discomfort is a common issue that affects many individuals, often impacting their quality of life. Understanding the various factors that contribute to knee discomfort is essential for effective management and prevention of this issue. In this article, we will delve into the common factors that can lead to knee discomfort, shedding light on the importance of identifying and addressing these factors.
Overuse and High-Impact Activities
One of the key factors contributing to knee discomfort is overuse and engaging in high-impact activities. Activities such as running, jumping, or repetitive movements can put significant stress on the knee joints, leading to discomfort and potential injuries. It is crucial to engage in such activities mindfully and incorporate proper rest and recovery to prevent overuse injuries.
Weight and Body Mass Index (BMI)
Another common factor linked to knee discomfort is excess weight and a high body mass index (BMI). Carrying excess weight puts added pressure on the knee joints, increasing the risk of developing conditions such as osteoarthritis. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help alleviate knee discomfort and reduce the strain on the joints.
Poor Posture and Alignment
Poor posture and misalignment of the body can also contribute to knee discomfort. When the body is not properly aligned, it can lead to uneven distribution of weight on the knees, causing strain and discomfort. Focusing on maintaining good posture and seeking professional guidance to address alignment issues can help alleviate knee discomfort and improve overall joint health.
Previous Injuries and Trauma
Individuals with a history of previous knee injuries or trauma are more susceptible to experiencing knee discomfort. These injuries can weaken the structures of the knee joint, making it more prone to pain and discomfort. Proper rehabilitation and ongoing care for previous knee injuries are essential to prevent recurring discomfort and maintain joint function.
Age and Degenerative Changes
As individuals age, degenerative changes in the joints can contribute to knee discomfort. Conditions such as osteoarthritis, which commonly affect older adults, can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling in the knees. Implementing preventive measures such as regular exercise, joint-friendly activities, and proper nutrition can help mitigate the impact of age-related degeneration on knee health.
Conclusion
Overall, knee discomfort is a prevalent issue that can significantly impact individuals’ daily lives. By examining the common factors contributing to knee discomfort, we have gained valuable insights into how to effectively manage and prevent this condition. It is evident that overuse and engaging in high-impact activities, such as running or jumping, can exert excessive stress on the knee joints, leading to discomfort and potential injuries. Mindful engagement in these activities coupled with adequate rest and recovery is crucial in preventing overuse injuries.
Furthermore, the correlation between excess weight, high BMI, and knee discomfort highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise. By reducing the pressure on the knee joints, individuals can alleviate knee discomfort and minimize strain. Addressing poor posture and body misalignment is also essential in preventing knee discomfort caused by uneven weight distribution on the knees. Maintaining proper posture and seeking professional guidance can significantly improve joint health and alleviate discomfort.
Moreover, individuals with previous knee injuries or trauma must prioritize proper rehabilitation and ongoing care to prevent recurring discomfort and maintain joint function. As age-related degenerative changes can contribute to knee discomfort, implementing preventive measures like regular exercise, joint-friendly activities, and proper nutrition is crucial for mitigating the impact of conditions like osteoarthritis. By addressing these common factors contributing to knee discomfort, individuals can proactively manage their joint health and enhance their overall quality of life.